Microwave Radio RTN950
Huawei Microwave Radio RTN950
Product Description
This document describes the product features, architecture, configuration, networking application, network management system, performance specifications of the OptiX RTN 950. With this document, you can obtain an overall understanding of this product.
Network Application
The OptiX RTN 900 is a new generation TDM/Hybrid/Packet integrated microwave transmission system developed by Huawei. It provides a seamless microwave transmission solution for mobile communication network or private networks.
Components
The OptiX RTN 950 adopts a split structure. The system consists of the IDU 950 and the ODU. Each ODU is connected to the IDU 950 through an IF cable.
Microwave Types
The microwave type is determined by the IF board and the configured working mode.
- SDH/PDH Microwave
The SDH microwave refers to the microwave that transmits SDH services. The PDH microwave refers to the microwave that transmits only PDH services (mainly, the E1 services). - Hybrid/Packet Integrated IP Microwave
The Hybrid/Packet integrated IP microwave (Integrated IP radio for short) can transmit one type among or a combination of Native TDM services, Native Ethernet services, and PWE3 packet services according to software settings. Therefore, the Integrated IP radio achieves a smooth upgrade from Hybrid microwave to Packet microwave.SpecificationEthernet service processing capabilityItem Description Ethernet service type - Native Ethernet services: E-Line service and E-LAN service
- PW-carried Ethernet services: E-Line service, E-Aggr service, and E-LAN (VPLS) service
Range of maximum frame length 1518 bytes to 9600 bytes VLAN - Adds, deletes, and switches VLAN tags that comply with IEEE 802.1q/p, and forwards packets based on VLAN tags.
- Processes packets based on the port tag attribute (Tag/Hybrid/Access).
- The VLAN ID ranges from 1 to 4094.
MAC address - The E-LAN service supports the MAC address self learning capability in two learning modes: SVL and IVL.
- MAC addresses can be filtered; that is, MAC addresses can be blacklisted.
- Static MAC address entries can be set.
- The capacity of the MAC address table is 16 k (including static entities and blacklist entities).
- The MAC address aging time can be configured.
Spanning tree Supports the MSTP protocol, and generates only the Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST). The functions of the MSTP protocol are equal to those of the RSTP protocol. IGMP Snooping Supported Link aggregation (LAG) Applies to the FE/GE port and microwave port.- Supports manual aggregation and static aggregation
- Supports load sharing and non-load sharing.
- The load sharing hash algorithm is implemented based on MAC addresses, IP addresses, or MPLS labels, and supports the specified mode and automatic mode.
Physical link aggregation (PLA) The physical layer aggregation (PLA) function and enhanced physical layer aggregation (EPLA) are supported at air interfacesPLA and EPLA are Layer 1 link aggregation group (L1 LAG) technology, which shares load based on the bandwidth at the physical layer to achieve link aggregation.A PLA group supports a maximum of two member links. An EPLA group supports a maximum of four member links.ERPS Supports ITU-T G.8032v1/v2-compliant single-ring or multi-ring network protection for Ethernet services. LPT Disables the remote Ethernet port that is connected to the user equipment when the transmission network or local port fails. QoS Supports QoS. For details, see QoS. Traffic control function Supports the IEEE 802.3x-compliant traffic control function. ETH-OAM - Supports IEEE 802.1ag- and IEEE 802.3ah-compliant ETH-OAM functions.
- Supports ITU-T Y.1731-compliant ETH-OAM functions, supports packet loss measurement, delay measurement, and delay variation measurement.
Ethernet performance monitoring - Supports IETF RFC2819-compliant RMON performance monitoring.
- Measures real-time and historical traffic and bandwidth utilization for ports.
- Measures real-time and historical performance events for DS domains, flows, VLANs, traffics on UNI side, PWs, and egress queues.
- Measures packet loss due to congestion for flows.
- Measures packet loss due to congestion for PWs and egress queues.
Synchronous Ethernet Supports ITU-T G.8261- and ITU-T G.8262-compliant synchronous Ethernet. EoPDH Supported. The EFP8 board provides the EoPDH function. EoSDH Supported. The EMS6 board provides the EoSDH function. There are two methods for mounting the ODU and the antenna: direct mounting and separate mounting.- The direct mounting method is generally adopted when a small- or medium-diameter and single-polarized antenna is used. In this situation, if one ODU is configured for one antenna, the ODU is directly mounted at the back of the antenna. If two ODUs are configured for one antenna, an RF signal combiner/splitter (hence referred to as a hybrid coupler) must be mounted to connect the ODUs to the antenna. illustrates the direct mounting method.The direct mounting method can also be adopted when a small- or medium-diameter and dual-polarized antenna is used. Two ODUs are mounted onto an antenna using an orthomode transducer (OMT). The method for installing an OMT is similar to that for installing a hybrid coupler.

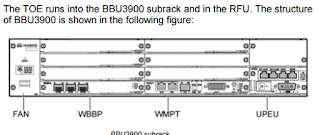
Fascinating post. I have been pondering about this issue, quite cool post. It’s actually great post. Thanks network management system
ReplyDelete